Environment

Reducing resource consumption and waste
| Reducing resource consumption and waste | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Strategic Goals | Aspects | Indicators | |
| • Technology and innovation • Operational excellence • Reduce energy, emissions and water consumption • Reduce waste and increase recycling • Engaging employees in environmental stewardship | • Operationalize at least three significant innovative product technologies that improve sustainable and healthy lifestyle choices by 2020. • Reduce consumption of energy, water and packaging materials by 15% per ton of product by end 2020. • Reduce greenhouse gas emissions per ton of product by 15% by end 2020 (2012 baseline). • Increase % of recycled waste from total waste by 15% by 2020. | • Materials • Energy • Water • Emissions • Effluents and waste • Products and services | G4-EN1 G4-EN3 G4-EN5 G4-EN8 G4-EN15 G4-EN16 G4-EN18 G4-EN20 G4-EN21 G4-EN22 G4-EN23 G4-EN31 | |
Preserve the planet
Reducing resource consumption and waste is a priority sustainability issue because we share the burden of responsibility with all other organizations and individuals to leave the planet in a condition which is fit for ongoing prosperity and quality of life for future generations. There is no doubt that climate change and weather extremes, dwindling resources, deforestation, soil erosion, water scarcity, overstuffed landfills, air pollution, excessive consumption and inadequate mechanisms for assuring the efficient use of resources and adoption of new agricultural and food technologies are all part of the same overriding threat to our long-term prosperity. As a corporate citizen driven by responsibility, we must do all we can to ensure we use only what we need, operate efficiently, manage our supply chain with accountability and minimize negative impacts on society and the planet. Our approach is based on the precautionary principle of analyzing environmental risks in our value chain and putting in place specific actions across our companies to ensure we mitigate these risks.
We continue to invest in improving our environmental management infrastructure and have increased our global environmental investments over the past four years, reaching a total of more than $21 million.
Strategy to action
Food technology innovation through our Alpha Strauss initiative
Technology and innovation is critical to improving the efficiency of our value chain. In some cases, innovation will lead us to develop entirely new products which offer breakthrough advantages in consumer experience and other tangible consumer benefit. In other cases, product and process enhancements achieved through technology will bring new ways of material consumption, manufacturing, logistics, packaging, shelf-life stability and more, which can make our entire value chain more efficient and help conserve resources. Technology is a key to healthy choices for our business and for our consumers.
Following the launch of Alpha Strauss last year, we continued to discover and invest in technologies for greater efficiencies in energy consumption, wastewater, and packaging. We also formed new partnerships with start-up companies and research facilities. Through these partnerships, we are getting closer to operationalizing new technologies for the benefit of the entire food industry and its consumers. Internally, we have nominated 32 Alpha Agents as specialist resources in our company that are available to support and progress innovative ideas. We hosted our second Alpha Strauss conference with participation of 150 entrepreneurs and representatives of investment funds and government officials.

Alpha Strauss MassChallenge: In 2013, our Alpha Strauss team and MassChallenge partnered to launch a food-focused accelerator program based in Israel. The program, drawing on our food technology expertise and the proven experience of MassChallenge in nurturing young companies and ideas, accepts entrepreneurs from around the world with food-tech related ideas or start-up companies. In partnership with MassChallenge, we will establish a food-tech Center of Excellence in in Israel, led by Alpha Strauss. The center will help entrepreneurs participate in the global MassChallenge program in the U.S., with an aim to attract more entrepreneurs and technologies and help position Israel as a powerhouse in food technology with global reach. This collaboration provides another platform for the Alpha community of entrepreneurs to develop their technologies and bring them closer to market.

Alpha Strauss innovation – biodegradable packaging: One current example of a potentially successful innovation supported by Alpha Strauss is a new form of flexible biodegradable packaging for food products. During 2013, we collaborated with the Israeli woman-owned start-up company, Tipa Corp. to help develop a flexible packaging product. Developing recyclable packaging options has been a challenge for the industry and in many cases, such as flexible packs for salty snacks, no viable solution has been achieved. In general, only 5 percent of salty snack packages tend to be recycled. With Tipa, we hope to revolutionize the sustainable packaging landscape.
Tipa Corp developed a unique multi-layered biodegradable film intended for the manufacture of flexible food and beverage packaging. Packaging materials based on the Tipa film are fully bio-degradable in 180 days, after industrial composting. Strauss and Tipa are currently collaborating on testing and matching this technology to packs of salty snacks, piloting the process in our salty snacks plant in Israel to produce the first commercial scale run of salty snacks in packaging based on Tipa biodegradable packaging film. We expect to be ready to go to market by 2015. Tipa’s technology and potential has already attracted much attention and, in early 2014, Tipa was successful in securing funding of $10 million from a new investor. We are pleased that the support provided by Alpha Strauss was able to contribute to this significant progress.
 Alpha Strauss innovation – wastewater treatment: Another unique innovation is currently being piloted through the Alpha Strauss community. In 2013, Strauss Israel collaborated with a start-up in wastewater technology, AMTR Scientific Ltd. to pilot an innovative wastewater treatment device. Our pilot program used a small mobile treatment device to test the technology on small amounts of water. The device is transferrable between our plants in Israel and its effectiveness can therefore be easily tested on different wastewater types. In 2013, the first pilot in our salads plant in Karmiel gave good results, reducing suspended solids and COD (chemical oxygen demand, an effective measure of water quality) way below regulatory limit. This has typically not been possible in standard wastewater treatment technologies. We plan to expand testing to more plants in 2014.
Alpha Strauss innovation – wastewater treatment: Another unique innovation is currently being piloted through the Alpha Strauss community. In 2013, Strauss Israel collaborated with a start-up in wastewater technology, AMTR Scientific Ltd. to pilot an innovative wastewater treatment device. Our pilot program used a small mobile treatment device to test the technology on small amounts of water. The device is transferrable between our plants in Israel and its effectiveness can therefore be easily tested on different wastewater types. In 2013, the first pilot in our salads plant in Karmiel gave good results, reducing suspended solids and COD (chemical oxygen demand, an effective measure of water quality) way below regulatory limit. This has typically not been possible in standard wastewater treatment technologies. We plan to expand testing to more plants in 2014.
Operational excellence
In 2013, within the context of our multi-year Operational Excellence program, which embraces continuous improvement in many parts of our supply chain activities, we placed a high focus on automation of processes to create greater efficiencies, production consistency and improved precision and quality. Additionally, automation removes much of the heavy manual work, such as lifting, which helps reduce risk of workplace injury. Since last year, we have mapped our entire operations in Israel to identify automation efficiency opportunities and adopted a five-year plan for implementation. In 2013, we implemented several programs in different facilities to add end-of-line robots to replace manual lifting of product cartons to pallets and for pallet transportation within warehouses. Another example is automated removal of products that do not meet quality standards from packing lines, improving accuracy and overall product quality levels.
Excellence in Australia: In 2013, we expanded our Obela manufacturing operations to Australia, establishing a manufacturing plant to deliver a variety of premium spreads and dips, including hummus-based spreads in different flavors such as roasted capsicum, zesty jalapeno and savory garlic. Our operations in Obela Australia now employ 70 people. We established our manufacturing operations in accordance with the same high operational excellence standards that we expect from our plants all around the world. In the first year of operation, Obela achieved impressive energy and emissions efficiencies.

Managing energy, emissions, water and waste
We continue to drive operational efficiencies and see opportunities to improve our environmental impacts through adopting new technologies and different ways of working. Throughout our different facilities around the world, our manufacturing operations seek to optimize production processes through identifying areas of opportunity to use fewer of the planet’s resources and divert more waste from landfill through recycling.
In our fresh salads factory in Karmiel in Israel for example, we achieved impressive results in 2013:
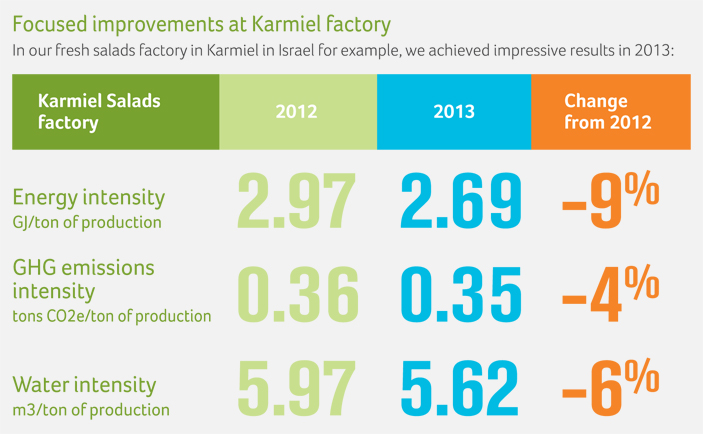
This was achieved through detailed attention to all aspects of resource consumption at every stage of the factory operation. Annual improvement targets in the factory are established by the nine-member factory management team, and resources are assigned for implementation of agreed plans. Actual consumption is monitored in real-time, enabling factory managers (and all operators in the factory) to see exactly how the factory is performing and identify problems as they occur, and take immediate corrective action. Progress is reported weekly to all factory employees.
In 2013, one project reduced energy consumption through a recalibration of air and cooling compressor control systems to attain maximum energy efficiency. Further energy savings were achieved by turning off non-essential systems at the weekend. For example, we changed the settings of our ice making system which normally works through the night, to stop during the weekend while the factory is not in production. Water savings were achieved in 2013 through a combination of equipment upgrades and process improvements. Filters on the vegetables washing system were changed to a higher quality alternative to avoid blockage, and improvements were made to the peeling processes to reduce water consumption.
Group energy, emissions, water and waste performance in 2013
Overall, our environmental results in 2013 do not fully reflect similar positive initiatives at Strauss plants around the world, with an increase in energy, emissions, water and waste levels on a group-wide absolute basis. We record overall impacts through our factories each year – we do not correct retroactively for addition of factories. In 2013, we added three sites in Europe to our overall operations and data collection that contributed 11.5% increase in overall energy consumption, most of our total increase in 2013. Similar effects were noted across other metrics. Not only this, one of the factories employs an unavoidably resource-intensive process for the manufacture of freeze-dried instant coffee, having little effect on production of just 2% of overall annual tons produced, but a far more significant effect on energy consumption, emissions and waste by 10%., 7.5% and 13% respectively. This caused our intensity measures to increase in 2013. We are working to improve this position.

Additional environmental initiatives in 2013
Strauss Coffee: carbon footprint analysis: In 2013, Strauss Coffee undertook carbon footprint assessment on two products, MK Café premium 250g product and Chyornaya Karta Gold 100g jar, to identify opportunities for reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Carbon footprint analysis measures the GHG emissions emitted directly and indirectly through the life cycle of a single product. For coffee, the entire carbon footprint includes emissions from coffee cultivation, transportation of coffee to production facilities, processing and packing at production facilities, retail distribution of the finished product, use of the coffee product by consumers in the coffee-making process in the home, and disposal of any residual coffee and packaging.
In this first analysis, we limited our scope to focus on those aspects of the coffee supply chain over which we have control and can reasonably collect reliable data. This relates to the stages included from the port of origin of the coffee to our finished goods warehouses, covering emissions from transportation of raw materials to the production facilities, emissions from direct fuel use and electricity use at the production facilities and emissions related to product packaging including emissions from production and transportation of the packaging.
Our first stage analysis helped us understand the differences in emission sources for different products, requiring tailored solutions for emissions reduction. In 2014, based on these analyses, we will focus on reducing GHG emissions during the coffee roast and grinding stages and also in the area of reducing packaging materials impacts. Later we intend to explore additional parts of the supply chain, including coffee cultivation and consumer use phases.
Strauss Water: Reducing energy consumption: We aim to minimize the environmental impact of our WaterBars throughout their lifecycle, and in 2013, we were delighted to confirm compliance of all our WaterBar models with the Energy Star certification program. Energy Star is a voluntary labeling program designed to identify and promote energy-efficient products. It is a joint program of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the U.S. Department of Energy. Energy Star certification is a way of confirming to our consumers that they have selected one of the most energy-efficient appliances available, both saving money in energy in their homes while supporting the sustainability of our planet.
In addition, at Strauss Water, we have been improving our packaging, replacing laminated filter packs with cardboard, along with other initiatives.
Max Brenner: Green disposable coffee cups: In 2013, Max Brenner launched “Fast Max”, a line of disposable takeaway packaging that is environmentally friendly. One cup consumed per day generates around 10 kilograms of waste packaging every year. As we sell more than 600 cups per day, the potential for landfill avoidance is over 6 tons per year.
The Fast Max line includes plastic cups and lids made entirely from plant sources, certified 100 percent compostable by the U.S.-based Biodegradable Products Institute. All of our different products now have environmentally friendly profiles – paper cups, coffee cup sleeves, trays and cookie bags are made with post-consumer recycled content and are recyclable, compostable and nontoxic. Printing uses water or vegetable-based inks. Now Max Benner customers can make positive choices for the environment as they enjoy their daily coffee and cookies.
Strauss Israel: Recycling since 2011: In Israel, we continue involve everyone in recycling through our partnership with the organization TerraCycle. In early 2014, we expanded the program to include plastic containers and bottles discarded after consumption of dairy products, collected in more than 100 locations around the country, yielding more than 2,000 packaging units in just a few weeks. Since 2011, more than 200,000 salty snacks packs were collected through the participation of schools and youth groups in over 650 collection points around the country. The unique TerraCycle model connects recycling with community involvement, encouraging consumers to bring their Strauss packaging waste to collection points throughout the country. At the same time, consumers select a social cause and Strauss Israel donates almost $3 for each 200 packs recycled. TerraCycle repurposes the materials received into affordable, innovative products.
Engaging employees in environmental stewardship
Our employees are critical ambassadors in our program to reduce environmental impacts and conserve resources. They play a big role in every aspect of our operations and help ensure we adhere to best possible environmentally conscious practices as we make and deliver our products. In 2013, we wanted to help educate and motivate our employees in Strauss Israel to do even more, by showing them how they can also benefit personally in their homes. In 2013, we launched our employee environmental program, “Think Green and Save Money”. The program aims to provide employees with tools to help them save money through reducing electricity consumption, water consumption, waste and increasing recycling. We conducted an employee survey addressing employee consumption habits and environmental behavior and provided recommendations for improvement based on the survey results. The 500 employees completing the survey received a financial incentive to support environmental investment in their own home.